const credentials = {
{ "ssid1", "********", "", "", ""} // no MQTT
, { "ssid2", "********", "10.14.0.1", "", ""} // MQTT without auth
, { "ssid3", "********", "10.0.0.111", "mqttuser", "********"} // MQTT with auth
};
```
Change the MQTT prefix and the topic names as you like. Currently the water counter value
is published in **watermeter/0/total** and so on.
```
#define MQTT_PREFIX "watermeter/0"
#define MQTT_total "/total"
#define MQTT_target "/target"
#define MQTT_ftemp "/flowtemp"
#define MQTT_atemp "/ambienttemp"
#define MQTT_info "/infocode"
```
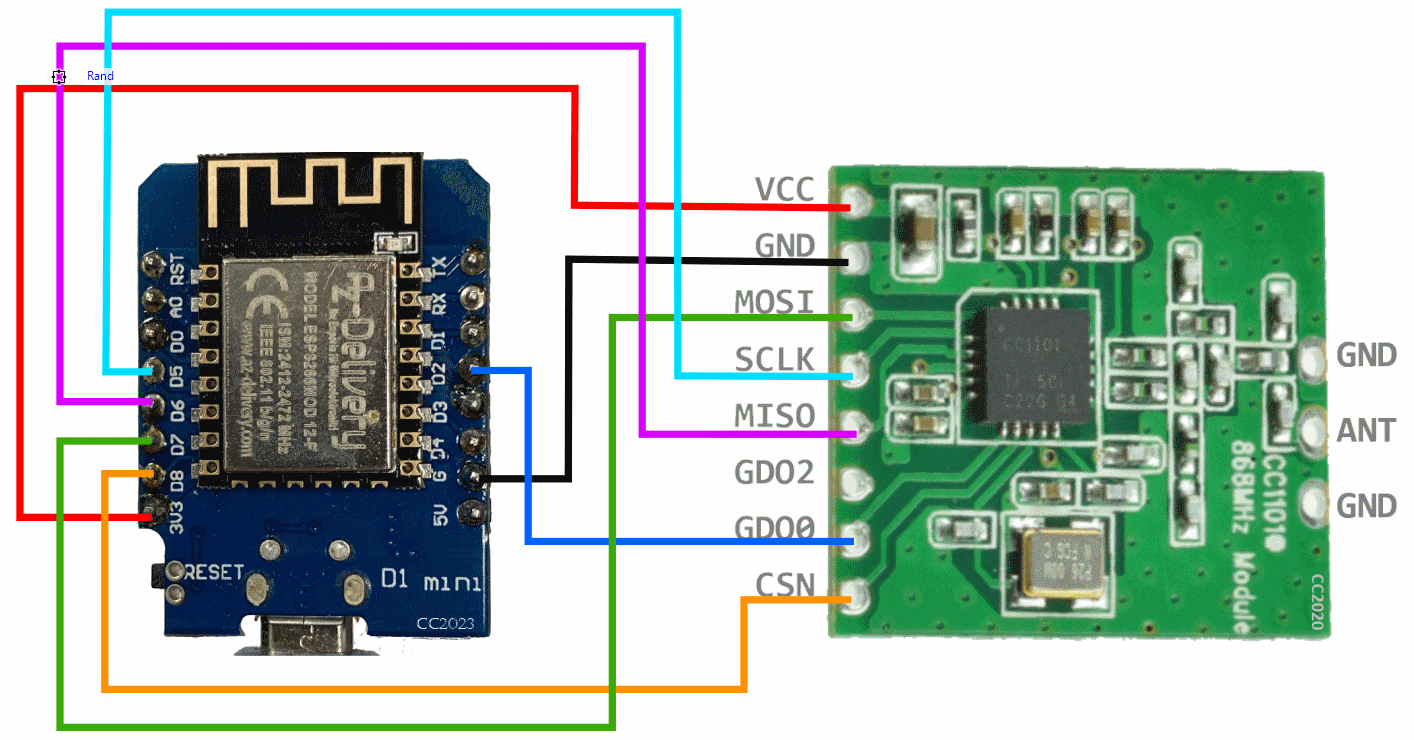
### Connect your ESP8266/ESP32 to the CC1101 868Mhz module:
| CC1101 | ESP8266 | ESP32 |
|--------|:-------:|:-----:|
| VCC | 3V3 | 3V3 |
| GND | GND | GND |
| CSN | D8 | 4 |
| MOSI | D7 | 23 |
| MISO | D6 | 19 |
| SCK | D5 | 18 |
| GDO0 | D2 | 32 |
| GDO2 | not connected| not connected|
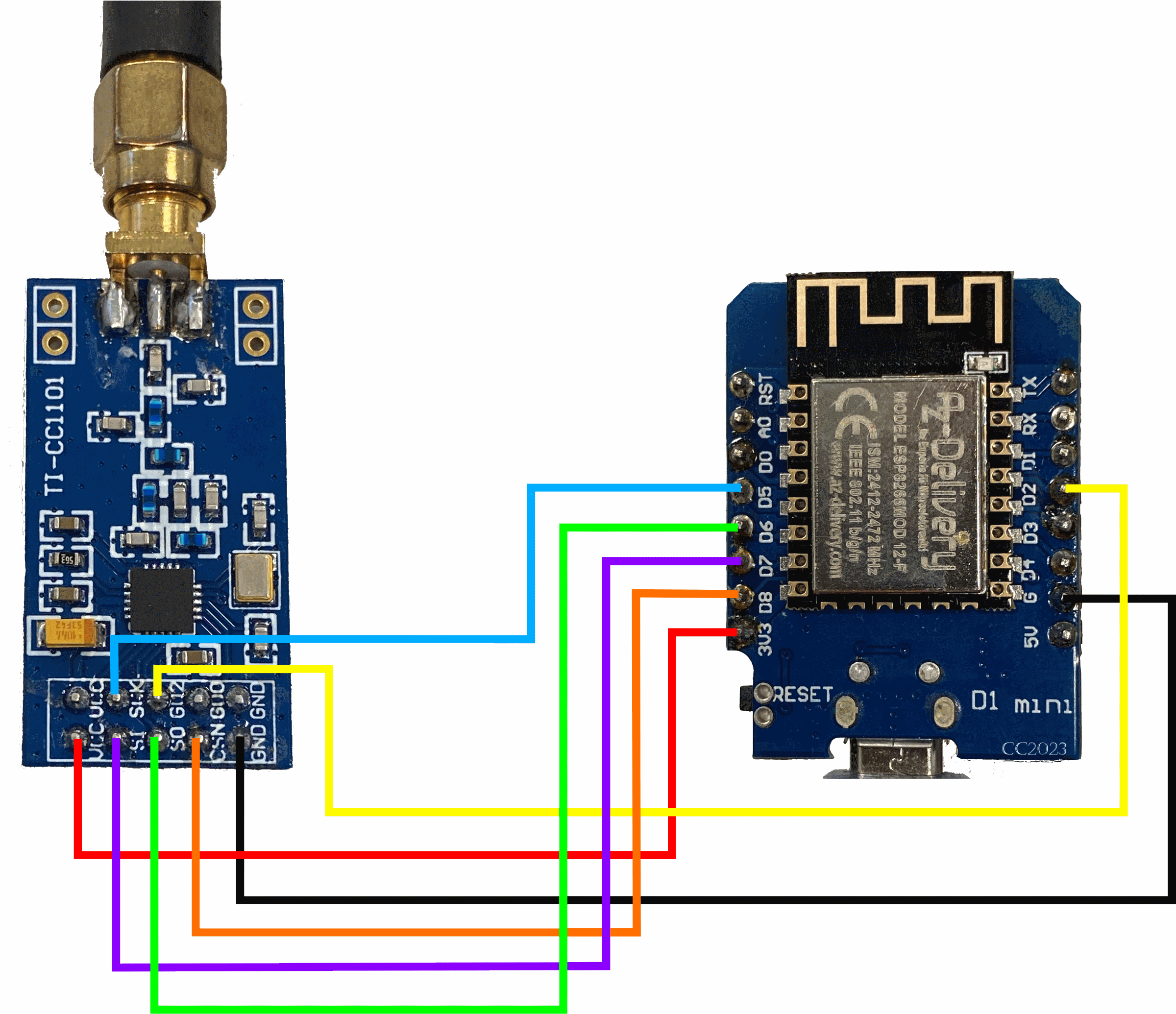
### D1 Mini connected to different CC1101 modules:
 ### Credit
Thanks to [weetmuts](https://github.com/weetmuts) for his great job on the wmbusmeters.
### Credit
Thanks to [weetmuts](https://github.com/weetmuts) for his great job on the wmbusmeters.

 ### Credit
Thanks to [weetmuts](https://github.com/weetmuts) for his great job on the wmbusmeters.
### Credit
Thanks to [weetmuts](https://github.com/weetmuts) for his great job on the wmbusmeters.
 ### Hardware
The hardware you need:
### Hardware
The hardware you need: